QR CODE
Contents
- 1 What's A QR Code?
- 2 Make Your Own QR Code
- 3 Some Examples Of QR Codes
- 4 QR Code Design
- 5 How Much Data Can A QR Code Store?
- 6 How Many Characters / Digits Can A QR Code Store?
- 7 Does a QR Code Have To Be Black And White?
- 8 Can QR Codes Be Inverted Or Mirrored?
- 9 Can a QR Code Be Rotated?
- 10 How Secure is a QR Code?
- 11 What Are The Different Sections In A QR Code?
- 12 QR Code Error Correction
What's A QR Code?
They are barcodes, very similar to the barcodes you’ve seen on almost every product you've bought. The main different between QR Codes and traditional barcodes, is that QR Codes can store many times more data in a much smaller area due to their ability to store data in 2 dimensions rather than 1. To name a few of QR Codes benifts:
- High Capacity - Require Less Space - Dirst And Damage Resistant - Readable From Any Direction
They started out very popular in the East but over the last 3 years have become ever more popular worldwide, this has been driven mainly by the fact they are so easy to scan as well as create. QR Codes are popping up everywhere and today they can be found in magazines, newspapers, product packaging and billboards. They are flexible, very cheap to create and the scope of use is very large. The purpose of a QR Code is to quickly and easily get data from a printed medium to a digital medium such as your smartphone. Compatibility is key to their rising popularity.
Make Your Own QR Code
The QR Code generator in the link below has been created by the Zxing project and is free to use via their website.
Please take the time to visit their homepage
Some Examples Of QR Codes
QR Codes hold many different types of data, with the naked eye you can’t tell what type of data a QR Code holds.QR Code scanner will process data differently based on its data type. This page contains examples of some of the more common data types which you can test on your Smartphone. You will notice that the different types of data behave in different ways. For example if the code contains a URL, the scanner is able to launch your browser with that URL, if it contains contact details then it can save them directly to your address book. This versatility offers a variety of uses for QR Codes.
- Some Examples Of QR Codes
QR Code Design
When you're creating a QR Code, you don't just have a grid of black and white squares to work with. You can use multiple colours and can also take advantage of error correction techniques built into the specification to embed images. Making your QR Code original, ensures that of the millions of QR Codes out there, people notice and take the time to scan yours. The reason images and logos can be displayed within QR Codes is mainly down to the built in error correction. The error correction allows up to 30% of a QR Codes to be corrupt while still remaining readable to a barcode reader. This means that you can use up to 30% of the QR Codes surface area to include your logo and designs.
- QR Code Design
- Samples
How Much Data Can A QR Code Store?
Unlike traditional barcodes, QR Codes are 2 dimensional allowing them to store a lot more data. The maximum amount of data a QR Code can store is 3Kb. A QR Code is made of up multiple rows and columns. These are seen by the naked eye as small squares, the combination of 177 columns and rows allows for a total of 31,329 squares. It's the arrangement of those squares in varying configurations that are able to store the data.
There are not 31,329 squares in every code. When a code is being created the generator determines the amount of data it needs to store and therefore the number of rows and columns needed to encode that data. If a QR Code contains more data, then you will generally find that it looks more dense(more squares and smaller squares). Similarly, turning on Error Correction within a QR Code increases the amount of data stored in a code and therefore the density. Here are some examples:
In addition to storing the intended content of the QR Code, the code must also store positioning, timing, alignment, format, error correct and version data to ensure it can be read easily by a wide range of scanners. Thankfully this is all built into the design of the QR Code and its only error correction that will subtract from the available 3Kb. It’s a common misconception that adjusting the surface area of a code will allow you to include more data. This isn’t true as increasing the surface area of your code will not allow you to have more than 177 columns and rows and so simply stretches the code.
How Many Characters / Digits Can A QR Code Store?
So we know that QR Codes store data up to 3Kb, but how does that translate into characters such as digits or text? When a QR Code is created, the user chose the encoding that is to be used and sets the type of data that the code will store. The chosen data type and encoding has a big impact on the number of characters that can be stored. As an example, if you were to create a QR Code that was only to contain alphanumeric data, then you would have the ability to encode up to 4296 characters.
| Numeric Only | Maximum 7089 characters |
| Alphanumeric | Maximum 4296 characters |
| Binary(8 bits) | Maximum 2953 bytes |
If you were to create a QR Code that would store binary data, then the number of characters you could store would reduce to 2953 as a result of the different type of encoding that would be used. This table details the maximum amount of data for each data type. These figures do assume that you’re able to use up all 3Kb of available space within your code, once you start to enable error correction at its various levels, it can reduce that amount of data that can be stored by up to 30%.
Does a QR Code Have To Be Black And White?
Although most QR Codes are black and while, they don't necessarily have to be this way. A QR Code can be any colour and can even include more than 2 different colours. There's examples of coloured QR Codes below.
Each QR Code is made of 2 types of small squares. This is most visible when looking at a black and while QR Code where squares are either black or white. For the purposes of this explanation, let’s call the black squares "foreground squares" and the white squares "background squares". While the image uses a variety of colours in order to stand out, it also ensures that all the colours used on the foreground squares are easily distinguishable from those used on the background squares. This means that your barcode reader won’t have any difficulty in picking up the foreground and background squares. Just by adding colour and a bit of design, designers have created some very interesting QR Codes.
Can QR Codes Be Inverted Or Mirrored?
One of the most common questions asked about QR Codes is can they be rotated or mirrored and still work. In short the answer is No. Mirroring a QR Codes or inverting it will prevent barcode readers from being able to decode the image and pull the data from within.
Can a QR Code Be Rotated?
Yes, A QR Code is omnidirectional and can be viewed / scanned any way around. Position detection patterns (Finder Patterns) help the scanner identify the correct way to read the image. This example is the same code in different rotated angles.
Each QR Code has 3 finder patterns that can be seen as large squares with a smaller solid square within. They are located in 3 corners of the QR Code. The 4th corner doesn't have a finder pattern and instead has an alignment pattern. This setup allows the scanner to determine the correct way to process the image (the corner with the alignment pattern is always the bottom right corner) allowing the scanner to effectively undo any rotation.
How Secure is a QR Code?
It would be easy to assume because of how basic a QR Code is, that few security concerns exist. There are however some areas in which QR Codes can pose a risk to your security. QR Codes are small harmless patterns printed onto a surface and their intent is only to help you get data from a printed medium to a digital medium. They cannot easily be read with the naked eye so they are particularly difficult to manipulate after publications. It would also expect that given their use is mostly to provide the user with a small snippets of information conveniently, that nobody would be interested in altering them or making them malicious? Well there are a couple of reasons and things to keep in mind. The first and probably main reason would be phishing. Phishing isn't just limited to e-mails, viruses or Trojans. In fact, using QR codes, unsuspecting users can be directed to malicious internet addresses and more. Contact details within the code can be modified so as to cause users to call or send SMS to a paid number.
What Are The Different Sections In A QR Code?
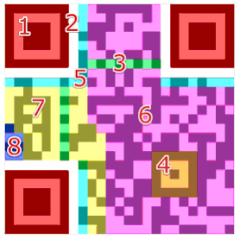
QR Codes are split into various sections and it’s these sections that the scanners use to decode the data. Below is a separation of each section. The image below is a standard text based QR Code. If you scan the code it should be decoded as text and will simply include the text "Sample QR Code".
- Section 1 - Finder PatternThe finder pattern consists of three identical structures that are located in all corners of the QR Code except the bottom right corner. Each pattern is based on a 3x3 matrix of black modules surrounded by white modules that are again surrounded by black modules. The Finder Patterns enable the decoder software to recognize the QR Code and determine the correct orientation.
- Section 2 - SeparatorsThe white separators have a width of one pixel and improve the recognizability of the Finder Patters as they separate them from the actual data. They are generally always white.
- Section 3 - Timing PatternAlternating black and white modules in the Timing Pattern enable the decoder software to determine the width of a single module.
- Section 4 - Alignment PatternsAlignment Patterns support the decoder software in compensating for moderate image distortions. Version 1 QR Codes do not have Alignment Patterns. With growing size of the code, more Alignment Patterns are added.
- Section 5 - Format InformationThe Formation Information section consists of 15 bits next to the separators and stores information about the error correction level of the QR Code and the chosen masking pattern.
- Section 6 - DataData is converted into a bit stream and then stored in 8 bit parts (called code words) in the data section.
- Section 7 - Error CorrectionSimilar to the data section, error correction codes are stored in 8 bit long code- words in the error correction section.
- Section 8 - Remainder BitsThis section consists of empty bits if data and error correction bits can not be divided into 8 bit code words without remainder.
QR Code Error Correction
Error correction can ensure that a QR Code remains readable when as much as 30% of the code is corrupt. Error Correction isn't always enabled. When a code is being created, it’s a decision to the users to specify if they want error correction to be enabled. There are 4 different settings. The higher the level of error correction built into the code, the less space there is for data to be stored. There are times when error correction is worth sacrificing storage space and times when it isn’t. For example, on a business card when you likely don’t need to store lots of detail, but where the card could become damaged or wet before the recipient has had a chance to scan it, the error correction could help. On the other hand, if you’re creating a code that will only be displayed digitally, the content of the code will not be damaged so error correction isn’t really needed. There are 4 different levels of error correction. These are: L[ow] (up to 7% damage) M[edium] (up to 15% damage) Q[uality](up to 25% damage) H[igh] (up to 30% damage). This error correction is achieved using "Reed-Solomon Error Correction" which in a very complex way is able to mathematically build in the backup data.